- Home
- About Us
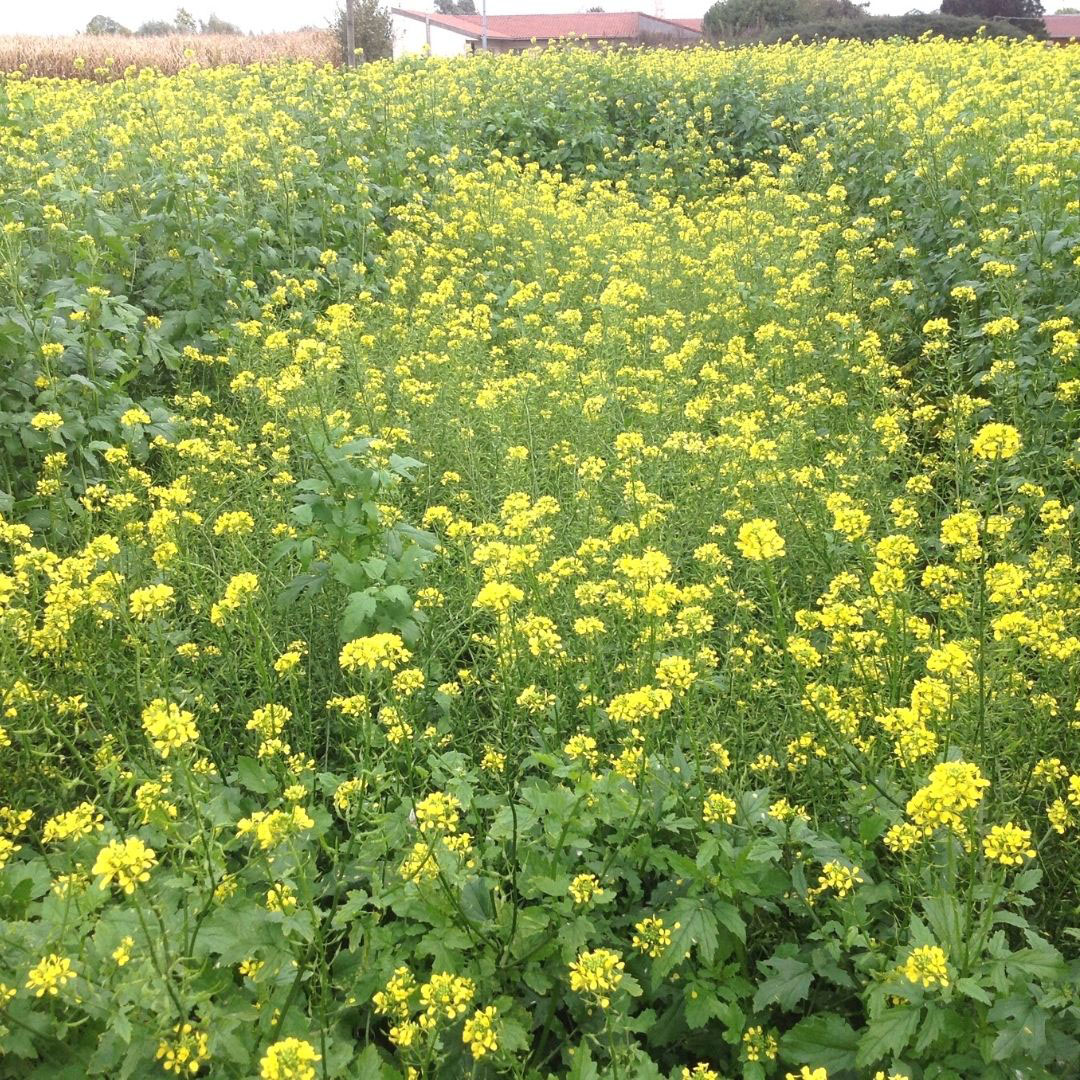
- Cover CropsThe adoption of cover crops is steadily increasing throughout the United States. Many industry experts see cover cropping as the way of the future. Conservationists point to cover crops as a necessary evolution in protecting soil and improving water quality. Leaving the soil undisturbed and keeping plant life growing for as many days out of the year as possible restores the natural cycles of the soil. Residue and roots create organic material in the soil, which serves as food to soil organisms. These organisms increase biological processes, that facilitate nutrient recycling and decrease nutrient loss caused by runoff.
- Turf
When it comes to finding the right product for your turf needs, it is important to look for qualities that address your specific climate, environment, use, and soil type. There is one quality, however, that must remain consistent no matter what the application is; your turf must be dependable.
Turf may be susceptible to an array of diseases such as rust, dollar spot, and pythium blight. Diseases like these can destroy an entire lawn. An excellent turf will not only be resistant to such diseases, it will have a quick recovery from wear and injury.
- Forage
Quality forages are an integral part of a profitable livestock operation; from planting to harvesting and grazing to healthier animals. We understand the importance of a productive and flourishing forage stand, no matter the climate or soil type.
- Collaboration
- News
- Home
- About Us
- Cover CropsThe adoption of cover crops is steadily increasing throughout the United States. Many industry experts see cover cropping as the way of the future. Conservationists point to cover crops as a necessary evolution in protecting soil and improving water quality. Leaving the soil undisturbed and keeping plant life growing for as many days out of the year as possible restores the natural cycles of the soil. Residue and roots create organic material in the soil, which serves as food to soil organisms. These organisms increase biological processes, that facilitate nutrient recycling and decrease nutrient loss caused by runoff.
- Turf
When it comes to finding the right product for your turf needs, it is important to look for qualities that address your specific climate, environment, use, and soil type. There is one quality, however, that must remain consistent no matter what the application is; your turf must be dependable.
Turf may be susceptible to an array of diseases such as rust, dollar spot, and pythium blight. Diseases like these can destroy an entire lawn. An excellent turf will not only be resistant to such diseases, it will have a quick recovery from wear and injury.
- Forage
Quality forages are an integral part of a profitable livestock operation; from planting to harvesting and grazing to healthier animals. We understand the importance of a productive and flourishing forage stand, no matter the climate or soil type.
- Collaboration
- News